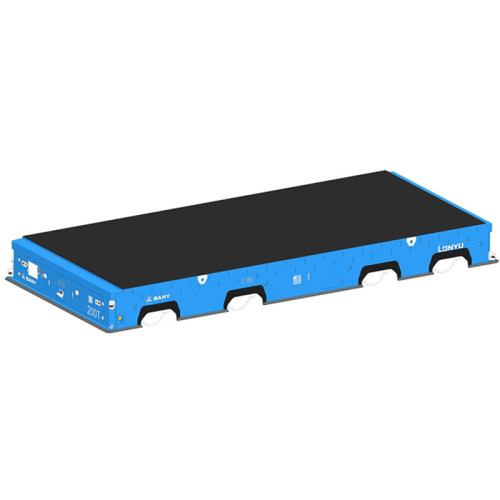
Indoor and outdoor handling of wind turbine main engine/drive system Automated guided vehicle system Heavy-duty AGV
- Model
- 24111A
Item specifics
- Rated load
- 200T
- Weight
- 30T
- Maximum vehicle dimensions
- 8210mm*3620mm*885mm
- Lifting stroke
- 200mm
- Gradeability
- ≤5°
- Operating environment
- Indoor and outdoor
- Navigation accuracy
- ±10mm
- Positioning accuracy
- ±10mm
- Protection level
- IP54
Review
Description
Automatic Guided Vehicle
Automatic guided vehicle systems, also known as an AGV system, otherwise known as an automated guided vehicle,autonomous guided vehicles, or even automatic guided cart, is a system that follows a predestined path around a facility. An AGV automated guided vehicle is a motorized vehicle that carries a load through either an assembly,manufacturing, or warehousing facility. An AGV can take on any form a customer requires to best address their application needs.
1.Magnetic Strip Navigation
Similar to electromagnetic guidance, magnetic stripe navigation uses magnetic stripe tape on the road surface instead of buried metal wires, achieving guidance through magnetic induction signals. This method offers greater flexibility, making it easier to change or expand the route, and the tape is simple to lay. However, this guidance method is susceptible to interference from surrounding metal objects and mechanical damage, making guidance reliability significantly affected by external factors.
2.Laser SLAM Navigation
Laser guidance involves installing precisely positioned laser reflectors around the AGV’s path. The AGV uses a laser scanner to emit laser beams and simultaneously collects the laser beams reflected by the reflectors to determine its current position and heading. AGV guidance is achieved through continuous triangulation. The biggest advantages of this technology are precise AGV positioning; no additional ground positioning equipment is required; and the driving path is flexible and adaptable to various field environments. It is currently the preferred advanced guidance method by many international AGV manufacturers. However, its disadvantages include high manufacturing costs, relatively stringent environmental requirements (such as ambient light, surface conditions, and visibility), and its unsuitability for outdoor use (especially due to rain, snow, and fog).
3.GNSS-GPS/Beidou Navigation.
4.Others—Ink ribbon, vision, and QR code.
The AGV drive system includes: wheels, servo motors, planetary reducers, chains, housings, slewing bearings, hydraulic cylinders/springs, etc.
Types of Automated Guided Vehicles
There are many different types of agv vehicles in use today.

Energy storage industry container applications
AGVs lurk beneath tooling stirrups, automatically raising and lowering to lift products. Within the production line, they can shuttle back and forth, transferring stirrup products and enabling flexible container production. Currently, they are being used by CIMC Energy, Geely Zeekr, and CATL.
Transformer Ultra-Thin, Ultra-Heavy-Duty AGVs:
Multi-motor coordinated omnidirectional drive
Multi-point hydraulic suspension and leveling system
Multi-sensor fusion navigation
Adaptability to diverse environments
Multi-vehicle linkage technology
Ultra-Thin Omnidirectional AGV (410mm)


Heavy-Load AGVs for the Wind Power Industry:
Using AGVs as the primary vehicle for building
modern, flexible production lines, the AGV system automates the production process and meets production
capacity
requirements.
IGV Unmanned Flatbed Truck – Intelligent
DrivingThis system utilizes a multi-sensor fusion perception solution, leveraging the sensing characteristics of
various sensor types to achieve full 360-degree coverage. The sensor fields of at least two sensors overlap
to
achieve redundancy.Easy to achieve 360-degree laser point cloud coverageSmall 3D blind spots for close-range obstacle detection


AGVs for flexible assembly lines for construction machinery (general engineering equipment, vehicle
engineering)
uild a modern, flexible production line using AGVs as the primary vehicle. Automated handling within the
production process is achieved through the AGV system, meeting production capacity requirements.② Design optimal assembly automation tooling based on assembly process requirements to ensure mixed-line
production of multiple vehicle models.